This site uses cookies to analyze visitor usage and improve usability.
For more information, please review ourcookie policyin our Terms of Use.
Please select “Agree” to continue browsing the site.
Research
Leading Research
― Creating “Future”―
We promote leading research and development towards realization of advanced aerospace missions and systems that create new value; i.e.
we create future from aerospace.
we create future from aerospace.
Research for Secure Development
and Success of Missions
and Success of Missions
― Connecting “now” to “Future” ―
We also support resolving challenges that the aerospace industry and projects face now using our expertise.
□□□□■ □□□□■
― □□□□■ □□□□■ □□―
□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■
Leading Research

Reduction in launch costs through the reuse of launch vehicles
Currently, we are conducting research towards the reuse of Japan’s flagship launch vehicles in future using a small-scale experimental vehicle (RV-X) as part of front-loading research activities for the experimental reusable vehicle (CALLISTO), which is being jointly researched by JAXA, CNES and DLR.
The plan is for RV-X to demonstrate the vertical take-off and vertical landing (VTVL) capability while reaching to the altitude of hundred meters. We aim to establish a method of operating the vehicle to be able to execute this series of VTVL sequences at high frequencies and short intervals.
The plan is for RV-X to demonstrate the vertical take-off and vertical landing (VTVL) capability while reaching to the altitude of hundred meters. We aim to establish a method of operating the vehicle to be able to execute this series of VTVL sequences at high frequencies and short intervals.
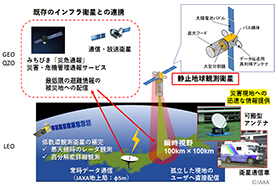
Earth observation system using Geostationary Orbit Satellites
With the conventional polar orbit Earth observation satellites, hour or day basis time is required from an observation request of observation to the data distribution, and therefore they did not always meet requests for urgent observation in times of disaster. Using geostationary orbit (GEO), we can make such instantaneous satellite observation possible. One of the largest technological challenges was to implement a large-scale telescope to keep useful ground resolution over the large disaster area from altitude of 36,000 kilometers.
In this study, we plan to apply the ground-based telescope mature technologies, e.g. the active optics system adopted by the Hawaii Subaru Observatory and the cutting-edge segmented telescope “Seimei Telescope” of the Okayama Astronomical Observatory in Japan, to materialize a large-scale space telescope. The target diameter of main mirror is 3.6 meters, which is more than double that of conventional optical spaceborne imagers. This achieves the ground sampling resolution of approximately 7 meters from GEO at nadir and an on-demand image/video Earth observation system within 30 minutes from the request. The Earth observation with these technologies, hence, can contribute to provide images instantaneously to end users, and to mitigate disaster damages.
In this study, we plan to apply the ground-based telescope mature technologies, e.g. the active optics system adopted by the Hawaii Subaru Observatory and the cutting-edge segmented telescope “Seimei Telescope” of the Okayama Astronomical Observatory in Japan, to materialize a large-scale space telescope. The target diameter of main mirror is 3.6 meters, which is more than double that of conventional optical spaceborne imagers. This achieves the ground sampling resolution of approximately 7 meters from GEO at nadir and an on-demand image/video Earth observation system within 30 minutes from the request. The Earth observation with these technologies, hence, can contribute to provide images instantaneously to end users, and to mitigate disaster damages.
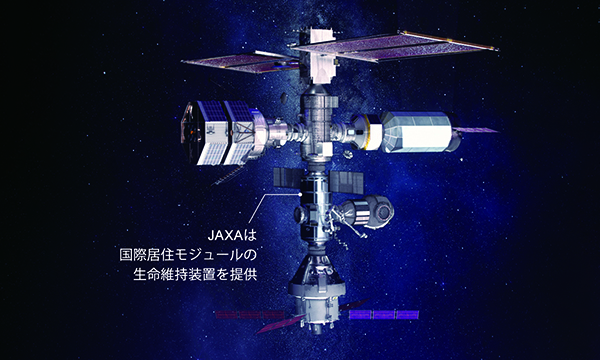
Research on space exploration
In December 2017, the space development strategy headquarters revised the process table for the Basic Plan on Space Policy, and stated, in regard to the international manned space exploration plan, that “in advance of a concrete international space exploration program, we will take the initiative to collaborate on unmanned explorations for space science exploration, and verify technologies in which Japan is superior and for which a ripple effect can be expected.” As concrete technologies, there are (1) gravity celestial landing technology, (2) gravity celestial surface exploration technology, (3) manned space state technology, and (4) deep space supply technology.
Meanwhile, the “total scenario for space exploration in Japan,” prepared by the JAXA international space exploration promotion team, presented a summary of the long-term vision, overall architecture draft, research objectives based on the abovementioned four fields, and a technology roadmap in addition to proposing space exploration scenarios in which Japan should be involved.
Meanwhile, the “total scenario for space exploration in Japan,” prepared by the JAXA international space exploration promotion team, presented a summary of the long-term vision, overall architecture draft, research objectives based on the abovementioned four fields, and a technology roadmap in addition to proposing space exploration scenarios in which Japan should be involved.
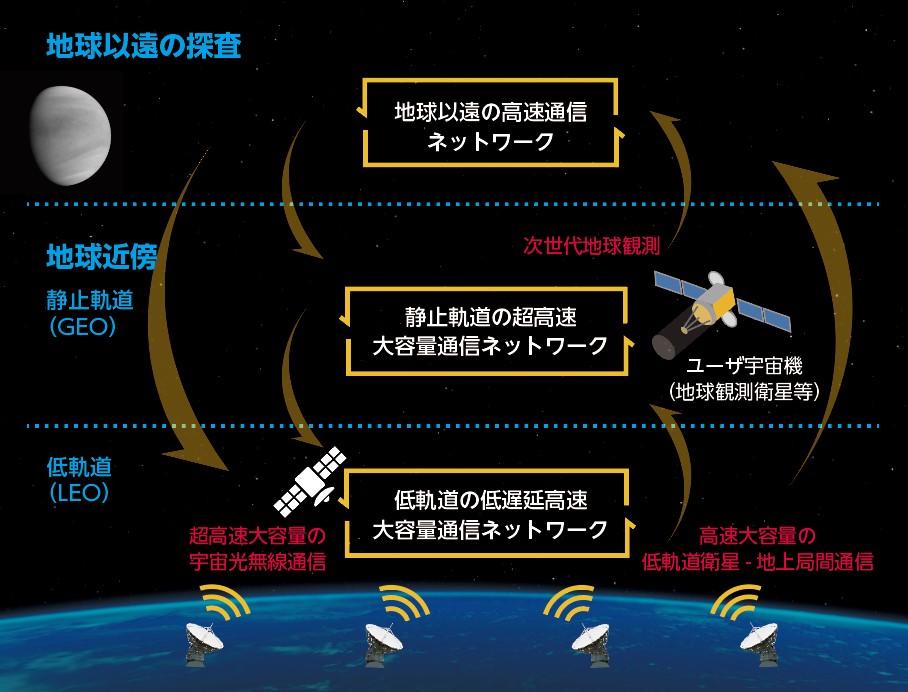
Low-cost, High-capacity, High-speed Satellite Communication System for Society5.0
For Society5.0, which, is the economic society following on from the hunter-gatherer society, agricultural society, industrial society, and information society, the transmission of information and highly flexible communications are required in broadband environments and in case of large-scale disasters over a wide range of fields of activity, including the sky and sea. Improving the line speed of satellite communications (geostationary communications satellites, earth observation satellites, and data relay satellites) is increasing in importance as a means of supporting these communications.
In this study, for the purpose of achieving a low-cost, high-capacity, high-speed communication satellite system, we research the communication payload, satellite bus, and ground systems respectively, across the wide range of the device level to system level.
In this study, for the purpose of achieving a low-cost, high-capacity, high-speed communication satellite system, we research the communication payload, satellite bus, and ground systems respectively, across the wide range of the device level to system level.
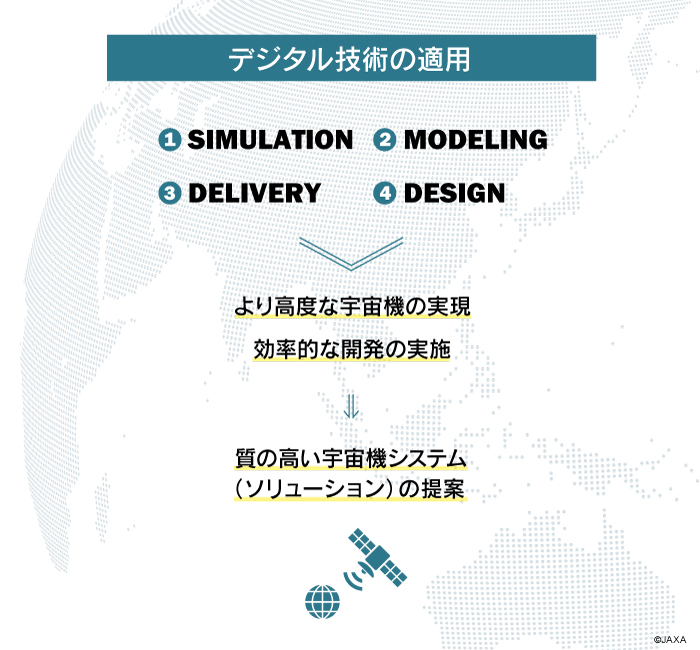
デジタル革命を牽引する次期技術試験衛星の研究
本研究では、非常に高いポテンシャルを有するデジタル技術を、衛星システムの開発から運用までのライフサイクル全体へ適用することによってコストの低減や開発期間を短縮し、また、システムの機能設計へ適用することによって、用途に応じて柔軟に仕様を変更できる機能や、より高度で複雑な機能を実現するための研究をしています。
Inter-disciplinary technology for increasing competitiveness and providing innovation in spacecraft that will create new fields of space use
Aiming to increase the international competitiveness of spacecraft, we are conducting cross-cutting research on innovative themes that lead to technological innovation.

航空機・将来宇宙輸送機への
水素燃料の適用技術研究
水素燃料の適用技術研究
□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □
Research for Secure Development
and Success of Missions
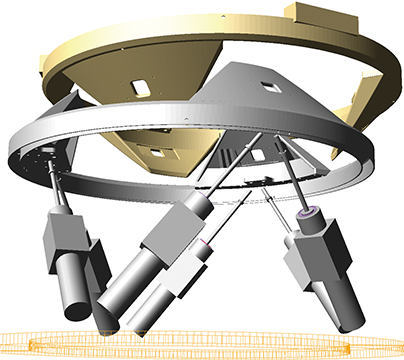
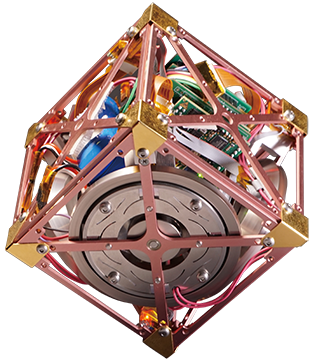
宇宙システム解析検証技術の研究
本研究は、世界最高レベルの情報・計算工学技術の研究・開発・利用により 、ロケットや宇宙機等のミッションの成功と開発期間・コストの低減を両立させるエンジニアリングを確立することを目標としています。
このエンジニアリングの確立により、現状では実現不可能な開発期間・コスト規模となるミッションを適切な規模で実現可能とします。またそもそも地上では困難な、極限の宇宙環境下でのシステム等の検証が実現できるという強みを獲得できます。
現有技術を活かし、新型ロケットH3やHTV等のプロジェクトの確実かつ効率的な実現を進めつつ、これと並行して、将来衛星や再使用輸送系等に向けた中・長期的な研究を行います。

革新的輸送系技術の研究
□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □
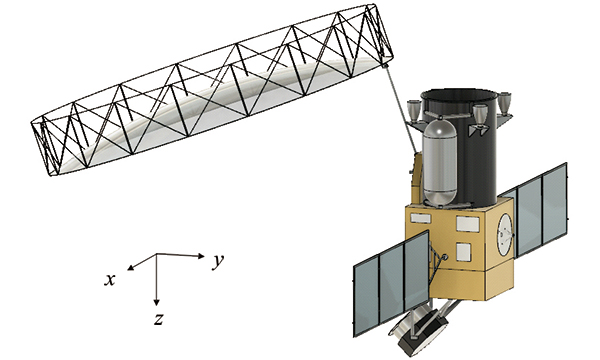
Research on the technology of space systems
A space system is a system of systems, consisting of many elements. It includes not only a launch vehicle and satellites but also ground segments such as the various ground facilities and installations. The mission success relies on the workings of the system as a whole, not on the discrete functions of its elements. In our research we will search for the most appropriate configuration of the elements in order to allocate a space system that will meet requirements for the system.
We will study various concepts of the space system, together with scientific expertise and technological capabilities in cooperation with internal and external bodies. Based on this study, we will propose a project that can pave the way to technologies that enhance Japan’s competitiveness, provide solutions to societal challenges, and enable strategies to secure industrial growth in the decades to come.
We will study various concepts of the space system, together with scientific expertise and technological capabilities in cooperation with internal and external bodies. Based on this study, we will propose a project that can pave the way to technologies that enhance Japan’s competitiveness, provide solutions to societal challenges, and enable strategies to secure industrial growth in the decades to come.
Research on earth observation sensor system
There are many types of sensors onboard Earth observation satellites. Spaceborne remote sensing instruments are broadly categorized according to the observation techniques they employ and the electromagnetic spectrums in which they operate (optical or microwave).
Utilizing comprehensive design engineering JAXA has acquired and accumulated for a sensor system, we have been researching key technologies and sensor systems expected to be required in the next decade or two. We have also been working with internal and external organizations to devise space missions that can fully benefit from the remote sensors to be developed in the future.
An ultimate goal is to translate our research findings into Operational Earth observation missions.
Utilizing comprehensive design engineering JAXA has acquired and accumulated for a sensor system, we have been researching key technologies and sensor systems expected to be required in the next decade or two. We have also been working with internal and external organizations to devise space missions that can fully benefit from the remote sensors to be developed in the future.
An ultimate goal is to translate our research findings into Operational Earth observation missions.
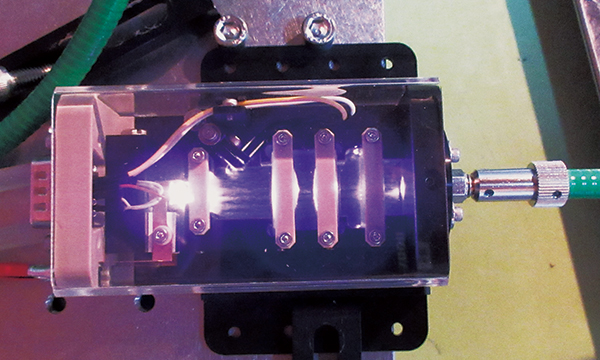
Research on space-qualified parts
Space-qualified parts, which have capability of withstanding the space environment, are indispensable for the reliable operation of a satellite over a long period in space. We have been researching and developing space-qualified parts essential to satellite development with two objectives: maintaining independent space programs and placing Japan's future satellites in a more competitive position.
We take a long perspective approach to R&D on space-qualified parts. Our scientists work with research institutes and private sectors to identify promising domestic technologies and focus our resources on the development of parts that we expect to provide innovative, effective solutions for future satellite systems. We intend to better translate our research into practical outcomes at the earliest stage possible.
We take a long perspective approach to R&D on space-qualified parts. Our scientists work with research institutes and private sectors to identify promising domestic technologies and focus our resources on the development of parts that we expect to provide innovative, effective solutions for future satellite systems. We intend to better translate our research into practical outcomes at the earliest stage possible.
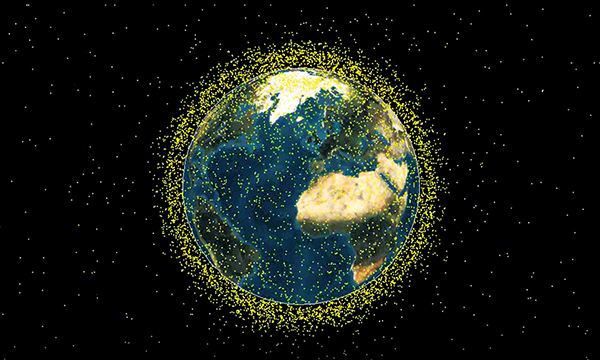
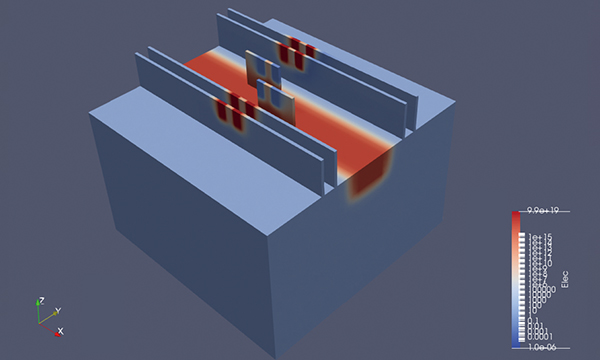
Ensuring the safety of space missions now and in the future
Space debris has been increasing year by year and in the future is expected to interfere with human space activities. To ensure the safety of space activities and promote sustainable space development in the future, JAXA is strengthening its cooperation with the government, as well as with internal and external related organizations, and is engaged in research and development of space debris.

宇宙活動拡大のための機構マテリアル基盤技術の高度化
□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □

ホールスラスタの競争力強化
□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □□□□■ □
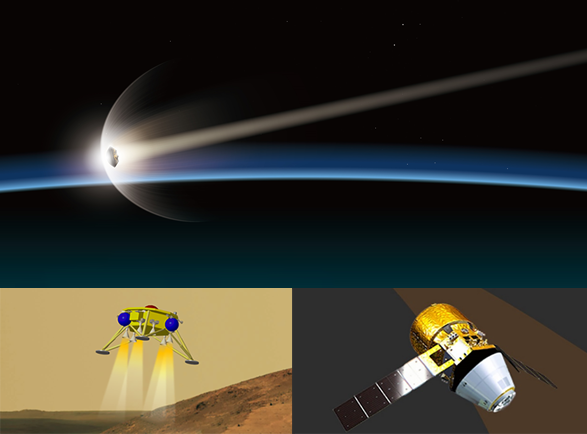

Research on Atmospheric Entry-Descent-Landing and Recovery (EDL&R) Technologies
In this research, we will support the projects currently under development in terms of technologies by organizing a cross-sectoral research team to share knowledge and to provide problem-solving schemes for issues related to the atmospheric entry systems and the take-off and landing systems for lunar and planetary exploration. In addition, we aim to produce the space missions that create new value by strengthening the common fundamental technologies essential for future advanced sample return missions, highly frequent and continuous flight demonstrators from LEO, and Mars exploration missions.
Project etc.

Innovative satellite technology demonstration program
The program is designed to offer access to space for commercial and institutional entities who wish to demonstrate innovative and new critical space parts or key technologies in orbit using their own microsatellites. The orbital demonstration will enable them to acquire and accumulate new findings and create future space missions and projects.
The program seeks to perform orbital demonstrations of innovative and new critical parts or key technologies using microsatellites in a timely and affordable manner, in order to ensure the continuous availability of critical space parts and the like as called for in the Basic Plan for Space Policy of the Government of Japan.
The program seeks to perform orbital demonstrations of innovative and new critical parts or key technologies using microsatellites in a timely and affordable manner, in order to ensure the continuous availability of critical space parts and the like as called for in the Basic Plan for Space Policy of the Government of Japan.
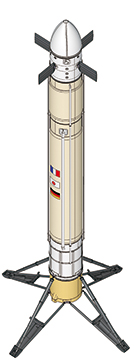
First stage reusability flight experiment (CALLISTO) project
We are engaged with research that aims to reuse the first stages of launch vehicles that previously have been disposable, as a method for securing further low costs and international competitiveness towards the realization of next generation of H3 launch vehicle.
The important technologies (key technologies) among those involved in the series of operations from launch to landing, and then reuse, have been identified. They are guidance and control technology, propellant management technology, and engine maintenance technology. Through the development of compact experimental vehicle and flight tests, we will accumulate knowledge related to these technologies.
While taking initiatives in technologies in which Japan has unique superiority, we also plan to proceed with efficient flight tests, based on international cooperation with French and German space agencies.
The important technologies (key technologies) among those involved in the series of operations from launch to landing, and then reuse, have been identified. They are guidance and control technology, propellant management technology, and engine maintenance technology. Through the development of compact experimental vehicle and flight tests, we will accumulate knowledge related to these technologies.
While taking initiatives in technologies in which Japan has unique superiority, we also plan to proceed with efficient flight tests, based on international cooperation with French and German space agencies.
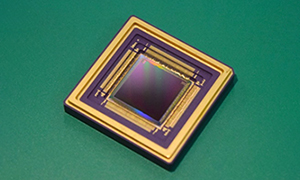
Development of SOI-SOC MPU
The evolution of information communications technology which realized the autonomous communication between “thing” and “thing” on a global network has enabled the world closely interconnected. It is considered that such a network will further extend into space in the future. Accordingly next-generation spacecrafts will demand even higher functionality and performance from space MPU (Micro processing Unit) which plays a core role of controlling information of the network under the harsh radiation environment of space.
JAXA are developing SOI-SOC MPU as the high-functionality/high-performance next-generation MPU, which adopts the SOI (Silicon on Insulator) semiconductor manufacturing technology and the SOC (System on Chip) design technology. Since the SOI technology is fundamentally superior in radiation tolerance and the SOC technology can load multiple functions on a single chip, SOI-SOC MPU will contribute to diverse and sophisticated space missions.
JAXA are developing SOI-SOC MPU as the high-functionality/high-performance next-generation MPU, which adopts the SOI (Silicon on Insulator) semiconductor manufacturing technology and the SOC (System on Chip) design technology. Since the SOI technology is fundamentally superior in radiation tolerance and the SOC technology can load multiple functions on a single chip, SOI-SOC MPU will contribute to diverse and sophisticated space missions.
Research on the Space Solar Power Systems (SSPS)
The Space Solar Power Systems (SSPS) convert energy from solar rays to either microwave or laser energy and transmit it from space to Earth for energy consumers. The system has the potential to solve important challenges facing humanity in areas, such as energy, climate change, and environmental conversion.
To develop the SSPS, we have been researching technologies for wireless power transmission by microwave/laser, and the assembly of large-scale structures. In addition, we have studied the SSPS comprehensively, including strategic approaches to research and development.
To develop the SSPS, we have been researching technologies for wireless power transmission by microwave/laser, and the assembly of large-scale structures. In addition, we have studied the SSPS comprehensively, including strategic approaches to research and development.

Commercial Removal of Debris Demonstration (CRD2)
Commercial removal of debris demonstrationc is the world's first technology demonstration of removing large-scale debris from orbit. This project is launched in collaboration with private sector, aiming to commercialize space debris removal and develop new markets for private business.

Multi-footprint Observation LIDAR and Imager mission (MOLI)
通常のカメラでは観測できない鉛直方向分布の観測が可能なライダー技術を用いた観測により、宇宙から森林バイオマスの高精度推定や高精度な地形情報取得に貢献します。

小型技術刷新衛星研究開発プログラム
- 開発期間の短縮や低コスト化につながる衛星の開発や製造方式の刷新(デジタライゼーション等)を目的として、超小型・小型衛星による短いサイクルでの技術開発と実証に取り組みます。 挑戦的な衛星技術の研究開発を推進し、その実証機会も確保していきます。
- 今後、政策・事業へのインパクトが大きい技術、我が国の宇宙活動の自在性確保にとって重要な技術を重点課題として識別し、取り組みます。
- 2024~2030年度の間、2年に1回の打上げを予定しています。